

M2052 damping alloy
Source: The Seishin Encyclopedia "Hosoya Pedia"
'' 'M2052' '' is
composed of manganese 73, copper 20, nickel 5, iron 2 (atomic
weight%) and has high vibration damping performance
Manganese alloy.
Under the vibration load, crystal twinning activity (occurrence,
disappearance, movement) occurs in the alloy,whereby
vibration energy is converted into thermal
energy and exerts vibration damping properties. It has
tensile breaking strength similar to that of mild steel,mostmolding
processes such as machining starting from
plastic working are possible,and the larger the amplitude
within the elastic limit The vibration damping
performance shows a high value.[1][2][3][4][5]
Index
|
Characteristic
As mentioned above, M2052 is
characterized by high vibration damping performance which
shows high value with larger amplitude within elastic
limit and versatility
which comes from free shape designability, so it is
natural that M2052 Various correspondence can be expected.
For example, in addition to
countermeasures against floor vibrations, internal
vibrations, chattering, damping and vibration isolation
in industrial machinery
and machine tools, measures to prevent Hakuro disease
bychainsawand shock buffering of air hammers, crushing
machines at construction sites
Electromagnetic induction
noise[note 1]caused by vibration in audio,
measuring instruments, and electronic equipment as well
as noise reduction, noise reduction and sound insulation
measures
against noises countermeasures, expected responses such
as sound insulation of silent sound of cars, ships, walls
and ducts of buildings, noise reduction,noise
reduction, etc. are diverse. Moreover, it can respond to
new vibration problems such as rolling shutter phenomenon
of camera image withdrone.
The features of M2052, etc., are effective elements for
countermeasures against vibration problems in various
fields.
History
The M2052 damping alloy has
a damping mechanism called a crystal twinning type and
has a property of extremely easy movement of the
transformation
twin boundary seen in the thermoelastic martensitic
transformation, so it exhibits a large damping capacity.
Sonostone, the same twinning type, was invented about 70
years ago and is still alive in military-related vessels.[1]
M2052 Damping alloy was invented and patented during research of Mn alloy from 1988 to 1995 at the National Institute for Materials Science and Technology.[6]
After that, in 1998,
application to audio accessories began as the Black Metal
and utilization of processability was utilizedInsulator,Screws,Washers,
Powder,
Sheet material Has been developed.[7]
Application examples first appeared in the industry are machine tool mounts announced by Seisin Engineering Co., Ltd. and packing for flanges of grinding wheels.[8]
However, the M2052 damping
alloy is easy to use and can design a free shape, but it
can not be said that it is still popular. There are
issues related to
the cooperation of the manufacturing organization of
materials and the proposed organization of applications (usage),
and issues relating
to the elimination of the cost increase due to small
volume production. Although there is a recent raw
material price, it is urgent to propose an application
that can balance the supply demand with the total demand
and to lower the price.
Recipe
M2052 damping alloy is
melted in the crucible at the raw material ratio of Mn 73,
Cu 20, Ni 5, Fe 2 (atomic weight%) and alloyed.
Dissolution is carried out
in a vacuum induction furnace filled withargongas and
becomes an ingot.
Next, billets are made by forging and processed into raw materials such as round bars and plate materials.
In the dissolution process,
it is important to manage O, N, S and C, and
contamination from crucibleand the purity of raw
materials
Mn, Cu, Ni, Fe, etc. It is a management point.
Classification of damping alloys
Damping alloys are
classified into four types from (1) composite type (2)
ferromagnetic type (3) transfer type (4) twin crystal
type from the viewpoint of
damping mechanism.
What has long been known as a structural member with damping properties is a composite cast iron, and is still active as a mother body and base of machine tools.
Ferromagnetic types of silentaroy (Fe - 12 Cr - 3 l, Toshiba) and Selena (Fe - 2.4 Al - 0.54 Si, NKK) are well known.
Transfer type magnesium alloy is lightweight.
Sinostone (Mn-37Cu-4.25Al-3Fe-1.5Ni,
Manganese Marine Co.) is used as a screw for military
vessels for sonar measures in the crystal twinning type.
Many of the twin crystal damping alloys represented by
Sonostone are well known alloys of Mn and Cu. The
amplitude dependence is linear,
and the vibration damping performance is proportional to
the amplitude, but the method of molding processing is
limited and it is used as a casting.
M2052 vibration damping
alloy belongs to twin crystal type, vibration damping
performance is proportional to the amplitude, parts can
be manufactured by
many processing methods while having characteristics.[1]
Characteristics of M2052 damping alloy
M2052 damping alloy has the following characteristics.
- Damping characteristics
correspond to wide stress, frequency and
temperature. In the elastic region, the higher
the amplitude,
the higher the vibration damping property is. The frequency can absorb vibration from <0: 01 Hz to 5 MHz. The use temperature is wide, from 4.2 to 375 K. - The strength is about mild steel and functions as a structural member.
- Excellent molding processability, product shape and size can be freely selected.
- Vibration damping performance has mass production performance of 0.2 ~ 0.3 in logarithmic decay rate.
- Damping properties are maintained even at helium liquefaction temperature, and ductility is not lost.
Mechanical nature
M2052 has the following mechanical properties.
Allowable stress:
- Tensile strength 540 MPa (compression)
- Longitudinal elastic modulus (3 point bending) 67.7 GPa
- Lateral elastic modulus[note 2](tensile) 17.8 GPa
- Poisson ratio (tension) 0.338
- Elastic limit (tension) 300 MPa
- Strength 0.2% (tension) 205 MPa
- Fatigue limit [Bending] (Stress) 160 MPa Distortion 5 × 105
- Hardness Hv 100 to 130
- Linear expansion coefficient[note 3](300 K) 22.4 × 10- 6
- Equivalent to specific heats[note 4](300 K) 512.7 J / Kg · K
- Thermal conductivity[note 5](300 K) 10 W / m · K
- Magnetic paramagnetic / antiferromagnetic[note 6]
- Density 7.25 gr / cm3
Amplitude dependence
Twin crystal
vibration damping alloys have characteristics that the
number of occurrences of twinning and movement increases
as the amplitude increases,
and the vibration absorption capacity increases due to
the twinning activity.
Frequency dependence
The vibration
damping performance by the frequency band has not
consistently measured data from 0.01 Hz to ultrasonic
range. Reference [1]
described by the inventor is a measurement result
based on the frequency sweep method performed in the
region of 75 Hz to 4.3 kHz[9],
The attenuation characteristic decreases as the
frequency decreases. Also, even in the high frequency
range of 3 to 5 MHz in the ultrasonic range,
a logarithmic attenuation factor of 0.7 or more was
obtained, which is similar to rubber.[10]
Temperature dependence
The vibration damping performance of the standard composition M2052 damping alloy deteriorates in the high temperature range with the limit of 80 ℃.
Further, researches are under way to shift the critical temperature to a high temperature by increasing or decreasing the composition of Mn, Cu, Ni and Fe.[1]
Processability
M2052 Damping alloy can be molded in various forms.
It is possible to perform
casting, welding, rolling, cold forging, wire drawing,
powder production, machining (cutting, grinding, etc.)
press working
which is a molding process for obtaining a shape
necessary for application.
Usage and application example
M2052 vibration damping alloy absorbs vibration energy by receiving vibration stress directly. Therefore, there is a method of directly sandwiching it in the vibration transmission path (serial insertion) and a method of placing it as a damper in the vibration transmission path (parallel insertion). In parallel insertion, there is also a method of adding a function of a composite vibration damping material such as a vibration damping steel plate by pasting a sheet material on the surface of the metal plate.
It can be said that M2052 which can produce free shapes, has simple amplitude dependence, can be applied to a wide range. However, it can not absorb large energy like an earthquake, and it is not adopted in the field where sufficient measures can be taken with rubber or resin.
M2052 Damping alloy began to be applied in the field of acoustic equipment and imaging equipment, and gradually spread to the field of countermeasures against chattering of machining machines and improvement of surface roughness.[11]
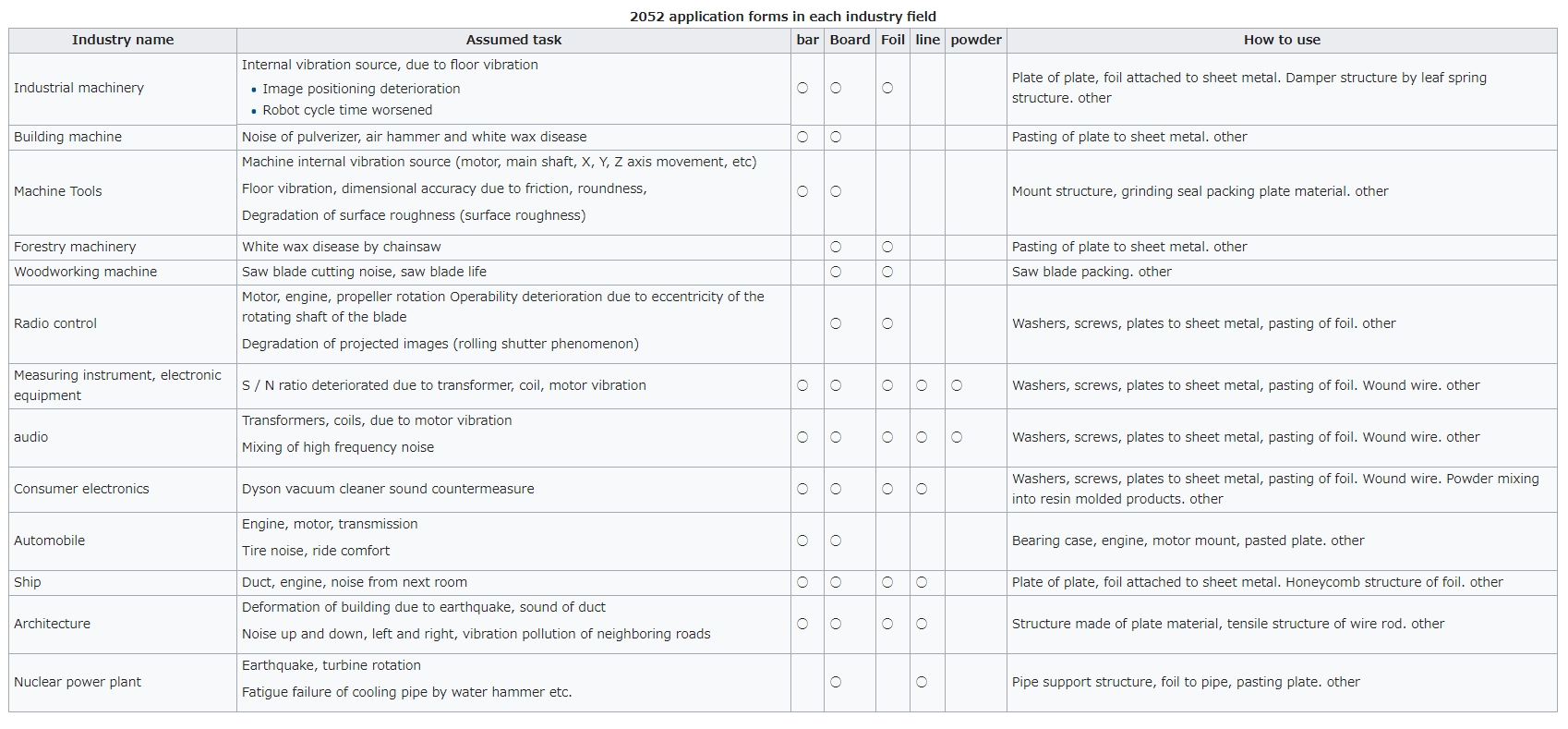
Footnote
- Note 1 Signal noise generated by Fleming's left hand rule
- Note 2 Calculated from Poisson's ratio
- Note 3 Equivalent to Al, Mg, Pb, Sn
- Note 4 Equivalent to Fe,Ni,Ti
- Note 5 Equivalent to Bi,Sb,Ti
- Note 6 Equivalent to Cr,Fe,In,Sn,Zn Magnetism is strongly affected by paramagnetism
Refernces
- [1][Kawahara
Koji: published by Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun,
Industrial Materials, 2004][The 2001
International Congress and Exhibition on Noise
Control Engineering The Hague, The Netherlands,
2001 August 27-30
The Damping Behavior and Practical Applications of the M2052 Damping Alloy] - [2] Koichi Sugimoto: Iron and steel, 60 (1974), 2203
- [3] Kenji Miura: Damping material (Ryohei Tanaka) Japan Standards Association (1992), 33
- [4]J.A.Hedley:MetalSci.J.,2(1968),129
- [5]F.Yin,Y.Ohsawa,A.SatohandK.Kawahara: MaterialsTrans.JIM,39(1998),841
- [6]Inventor: Koji Kawahara, Applicant: Independent Corporation Institute for Materials and Materials, Patent 2849698
- [7]A & V Village, No. 33 (1998) ~ A & V Village, No. 61 (2003)
- [8]Takeshi Hosoya: Monthly functional material September 2004: Improvement of grinding performance by installation mount made of damping alloy M2052
- [9]F.Yin,S.Takamori,Y.Ohsawa,A.SatohandK.Kawahara:Proc.onNoiseCont.Eng. p995,2001,Aug.,Netherland
- [10] Fukuhara Mikio, Yin Fuku star, Kawahara Koji: physicastatussolidi
- [11]Inventor Takeshi Hosoya et al., Applicant Co., Ltd. Seishin Engineering, Published Patent 2002-146498
External link
- M2052 laboratory - Homepage of the research laboratory that has been involved from application to manufacturing method for 20 years from the dawn of M2052